Allergies are a widespread health concern, affecting a significant portion of the global population. Various substances, such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods, can trigger these immune system reactions. Recognizing common allergy symptoms and knowing how to treat them effectively can greatly improve the quality of life for those who suffer from these conditions.
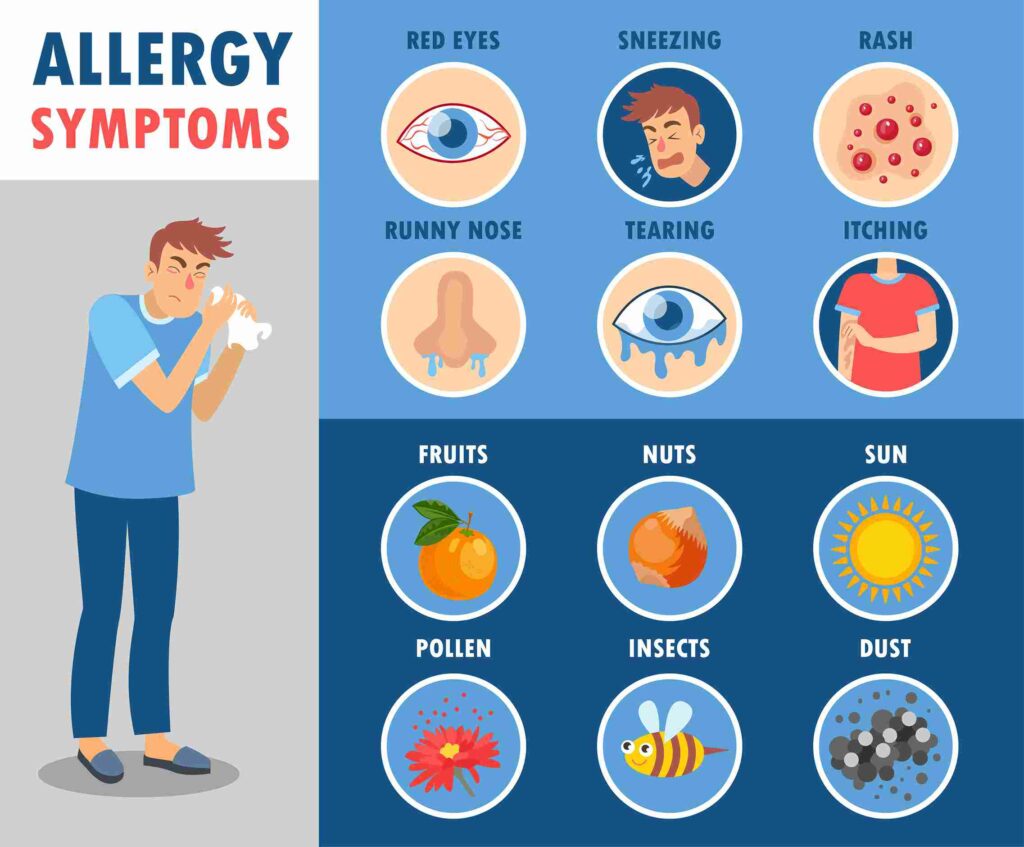
Common allergy symptoms:
Allergy symptoms can range from mild to severe and may affect different parts of the body. Some of the most common symptoms include the following:
1. Respiratory symptoms: Sneezing, runny nose, nasal congestion, and postnasal drip are typical signs of respiratory allergies, such as hay fever (allergic rhinitis).
2. Eye symptoms: Itchy, watery, and red eyes are common in those with allergies, particularly when exposed to airborne allergens like pollen or pet dander.
3. Skin symptoms: Allergic reactions can cause skin irritation, rashes, or hives (urticaria). Contact with an allergen or ingestion of a food allergen can trigger these symptoms.
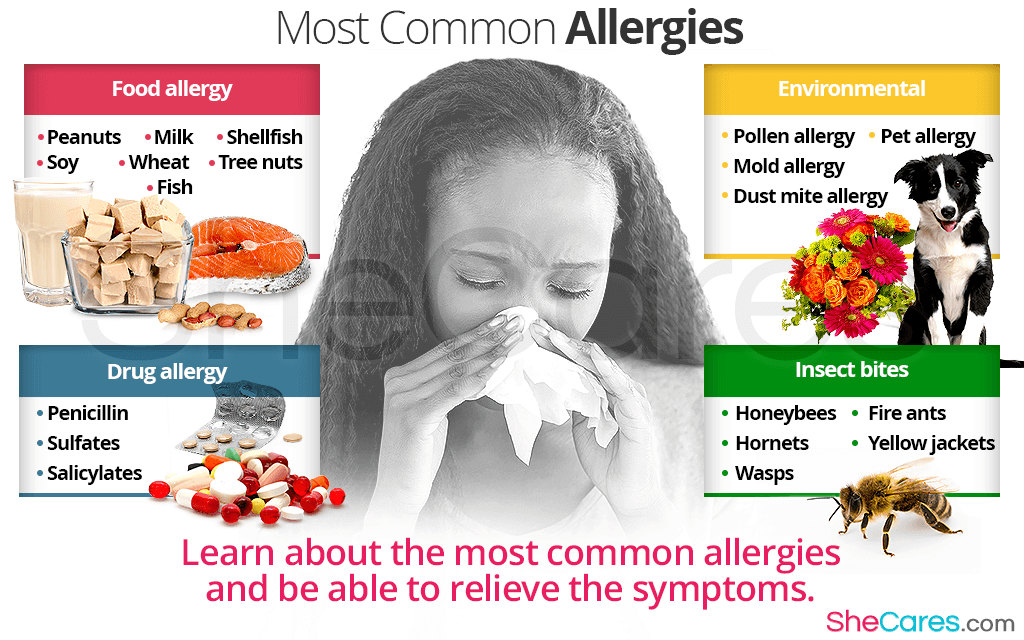
4. Gastrointestinal symptoms: Food allergies can cause stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In severe cases, food allergies may lead to anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening reaction.
5. Asthma symptoms: Allergies can trigger or worsen asthma symptoms, such as wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing.
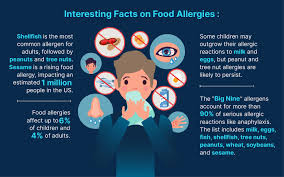
Diagnosing Allergies:
If you suspect that you have an allergy, it is essential to consult with your primary care physician or an allergist. They will take a detailed medical history and may recommend one or more of the following tests to identify the specific allergen(s) causing your symptoms:
1. Skin prick test: This test involves placing a small amount of the suspected allergen on the skin and then pricking the skin to allow the allergen to enter. If a red, itchy bump appears, it indicates an allergy to that substance.
2. Intradermal test: Similar to the skin prick test, this test involves injecting a small amount of the allergen under the skin. When a skin prick test is negative but the doctor still suspects an allergy, they often use this test.
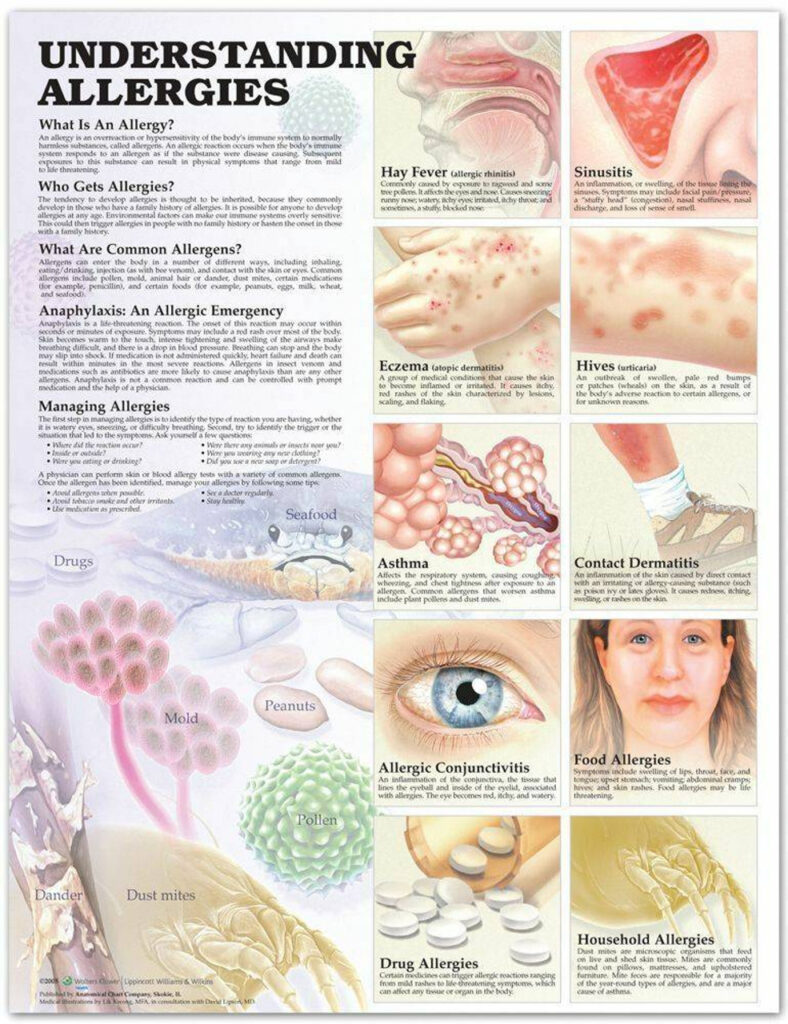
3. Blood tests: Specific IgE (sIgE) tests measure the antibodies produced by the immune system in response to specific allergens. These tests can be helpful when skin tests are not possible or when the results are unclear.
Treating Allergies:
The most effective way to manage allergies is to avoid the allergen(s) whenever possible. However, complete avoidance is not always feasible. In such cases, several treatment options are available:
1. Medications:
a. Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines like loratadine (Claritin), cetirizine (Zyrtec), or fexofenadine (Allegra) can help relieve symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. For more severe symptoms, doctors may recommend prescription antihistamines like levocetirizine (Xyzal) or desloratadine (Clarinex).
b. Decongestants: Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) or phenylephrine can help reduce nasal congestion. Over-the-counter allergy medications often combine these medications with antihistamines.

c. Nasal corticosteroid sprays: Prescription nasal sprays like fluticasone (Flonase), mometasone (Nasonex), or budesonide (Rhinocort) can reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and provide relief from symptoms.
d. Eye drops: Antihistamine eye drops, such as ketotifen or olopatadine, can help relieve itchy, watery eyes.
e. Leukotriene modifiers: Montelukast (Singulair) is a prescription medication that can help with both allergies and asthma by blocking the action of leukotrienes, which are inflammatory compounds released during an allergic reaction.
2. Immunotherapy: We may recommend immunotherapy for individuals with severe or persistent allergies who do not respond well to medications. This treatment involves gradually exposing the person to increasing amounts of the allergen to build up tolerance over time. You can administer immunotherapy through allergy shots (subcutaneous immunotherapy) or sublingual tablets or drops (sublingual immunotherapy).
3. Emergency treatment: In the case of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), immediate use of an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) is crucial. Seeking emergency medical attention is the next step, given the life-threatening nature of anaphylaxis.

Lifestyle Changes:
In addition to medical treatment, making certain lifestyle changes can help minimize exposure to allergens and reduce symptoms.
1. To improve indoor air quality, use air filters like high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and regularly vacuum with a vacuum cleaner that has a HEPA filter.
2. Bedding: To reduce dust mites, wash bedding weekly in hot water (at least 130°F or 54°C). Consider using allergen-proof covers for pillows, mattresses, and box springs.
3. Pollen avoidance: During high pollen days, keep windows closed and use air conditioning to filter the air. Check local pollen counts, and try to stay indoors when counts are high.
4. Personal hygiene: Shower and change clothes after spending time outdoors to remove pollen from your hair and skin.
5. Nasal irrigation: Using a nasal rinse or neti pot with a saline solution can help flush allergens from nasal passages, reducing symptoms.
6. Pet allergies: If you have a pet allergy, keep pets out of the bedroom and off the furniture. Regular pet grooming and bathing can also help to reduce allergens.
Conclusion:
Allergies can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications, you can effectively manage your symptoms. If you suspect that you have an allergy, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized allergy management plan. Understanding your triggers and taking proactive steps to minimize exposure and treat symptoms can help you lead a more comfortable and enjoyable life despite your allergies.
Images are obtained online.


